Electrolytic reduction and Electrolytic refining
1. What is the difference between Electrolytic reduction and Electrolytic refining?
Ans: ELECTROLYTIC REDUCTION:
The salts of these metals like chlorides in molten form are electrolysed. Metal is deposited at the cathode ( negative electrode) and chlorine is liberated at the anode ( positive electrode).
The reactions are as follows:
At cathode Na+ + e- → Na ( Reduction)
At anode 2Cl- → Cl2 + 2e- (Oxidation)
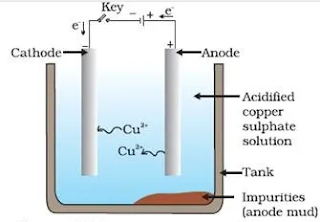
ELECTROLYTIC REFINING:
It is the process of purification of the metal obtained after reduction. Various methods for refining are employed, but the most common one is the electrolytic refining.
Process:
1. In this process, a thick block of impure metal is used as anode.
2. A thin strip of pure metal is used as cathode.
3. A solution of metal salt is used as an electrolyte.
4. When electric current is passed, metal ions from the electrolyte are reduced as metal which get deposited on the cathode.
5. An equivalent amount of pure metal from the anode get oxidised to metal ion and goes into the electrolyte and from there it goes to cathode and deposit.
6. This cycle is repeated until whole of the metal ion from impure block is dissolved and deposited on cathode.
7. The soluble impurities go into the solution, whereas the insoluble impurities settle down below anode and are known as anode mud.
Example 1: In electrolytic refining of crude copper.
Anode electrode: Impure copper
Cathode electrode: Pure copper
Electrolyte: Copper sulphate solution
Example 2: In electrolytic refining of crude unknown metal M
Anode: Impure M
Cathode: Pure M
Electrolyte: M sulphate of solution


No comments:
Post a Comment